normal end tidal co2 after intubation
The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Remember CO 2 is a result.

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Likewise case studies have shown that patients with a high initial end tidal CO2 reading were more likely to be resuscitated than those who didnt. Sensor links to monitor displays numeric ETCO 2 and waveform.
The document has moved here. Age gender vital signs laboratory findings are recorded. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
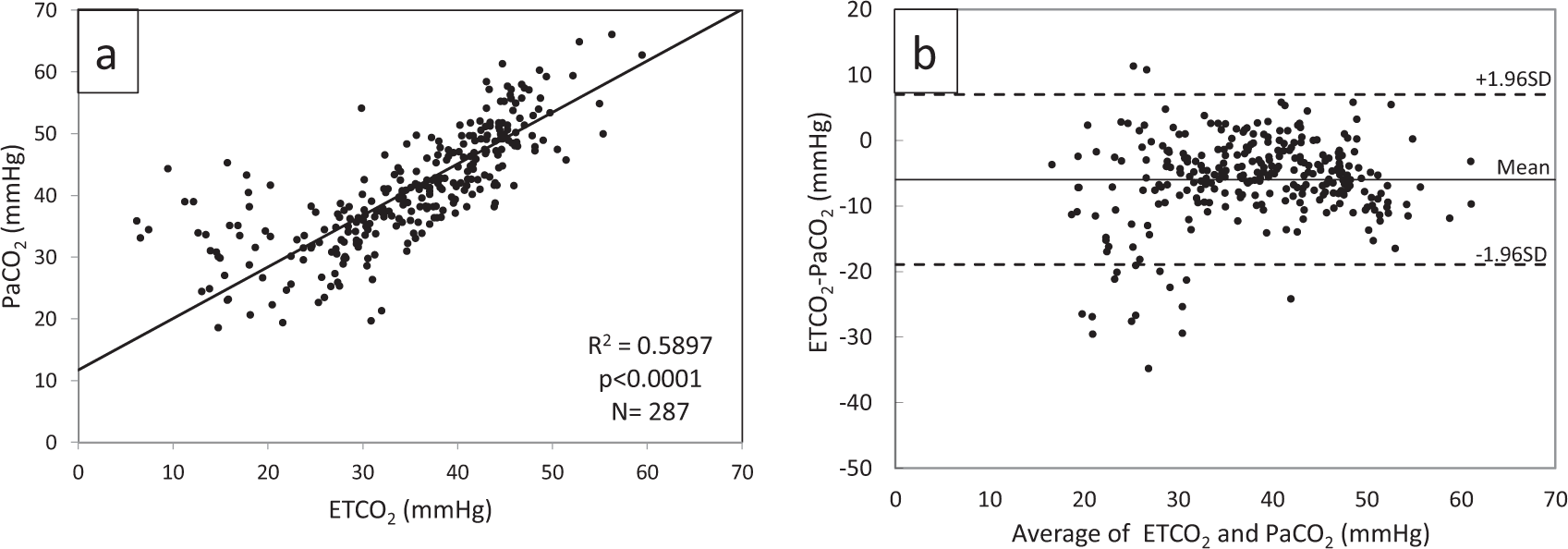
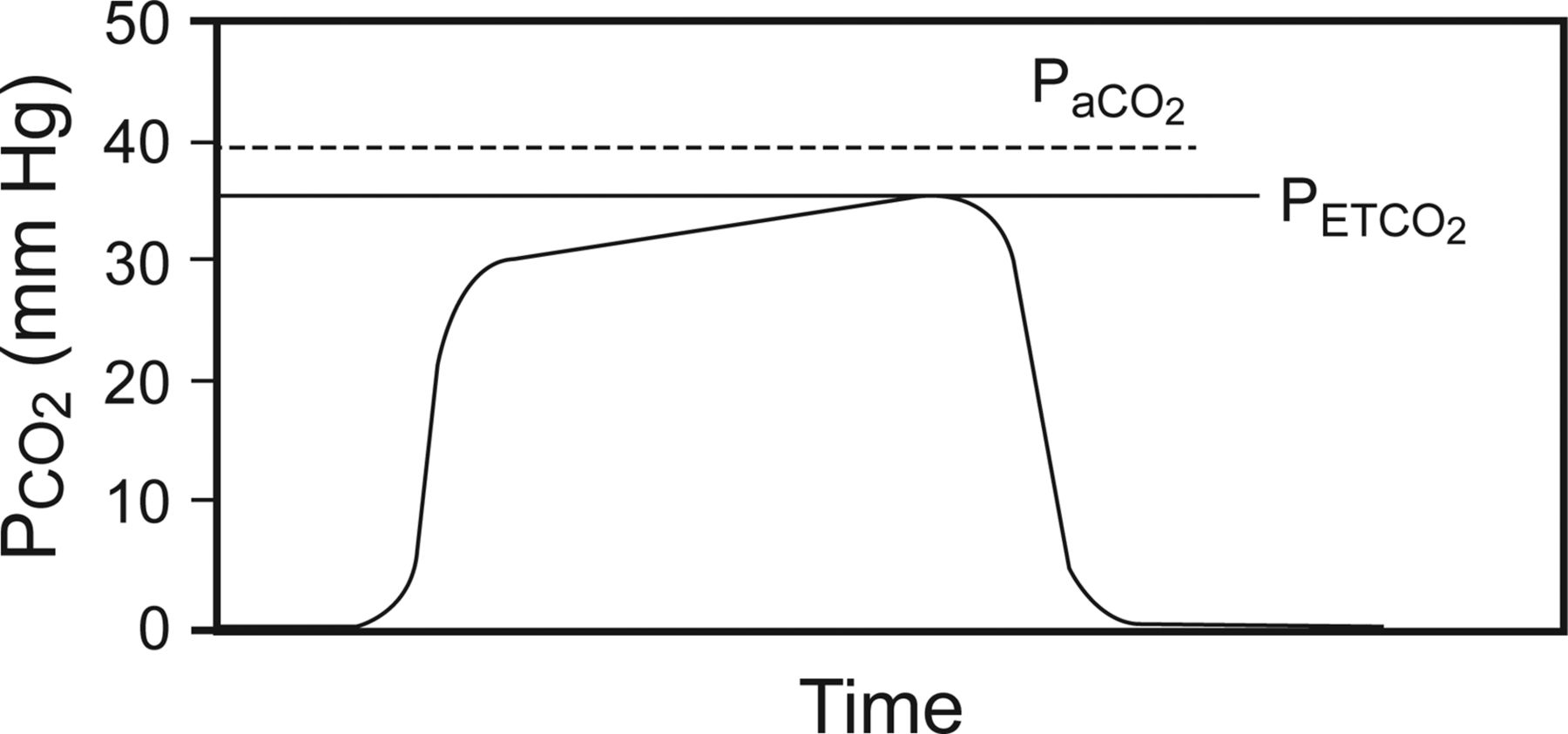
Further fine tuning of the American Society of Anesthesiology published. Immediately after intubation as measured by the capnography the initial PETCO2_1 and at post-ventilation 15 min PETCO2_2 and first second arterial blood gas analysis are recorded. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
Although the normal range for CO2. ASA Standards Amended. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG.
After placement of the endotracheal tube an end-tidal carbon dioxide recording of 35 mm Hg with a normal square wave tracing was observed on the Datex monitor Datex Helsinki. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.
End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output. 428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. C02 Seen After Intubation Now the Standard of Care.
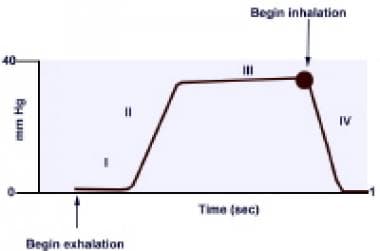
A normal trace appears as a series of rectangular waves in sequence with a numeric reading capnometry that shows the value of exhaled CO2. End Tidal CO 2 5 Continuous PETCO 2 in line between airway and BVM or ventilator circuit. The greater the initial value the likelier the.
An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2. In thromboembolism ETCO2 is significantly lower than normal due to the reduction of pulmonary perfusion and increased alveolar dead space that reduces the amount.
End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a. Changes in end-tidal carbon dioxide and volumetric carbon dioxide as. Changes in the shape of the capnogram are diagnostic of disease conditions while changes in end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 the maximum CO 2 concentration at the end of.
Normal ETCO2 is in the.

Effect Of Tidal Volume And End Tracheal Tube Leakage On End Tidal Co2 In Very Low Birth Weight Infants Journal Of Perinatology

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring For The

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Etco2 In Cpr
End Tidal Capnography Background Indications Technical Considerations

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Learn More With This Respiratory Article By Melissa Marshall

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
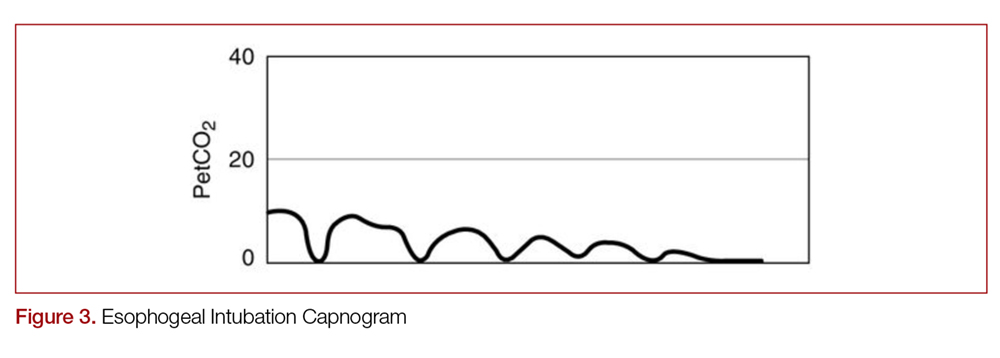
End Tidal Capnography In The Emergency Department Mdedge Emergency Medicine

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Etco2 In Cpr

Etco2 In Non Intubated Patient A Must In Ed
Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Respiratory Care

Monitoring Exhaled Carbon Dioxide Respiratory Care

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring For The

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4
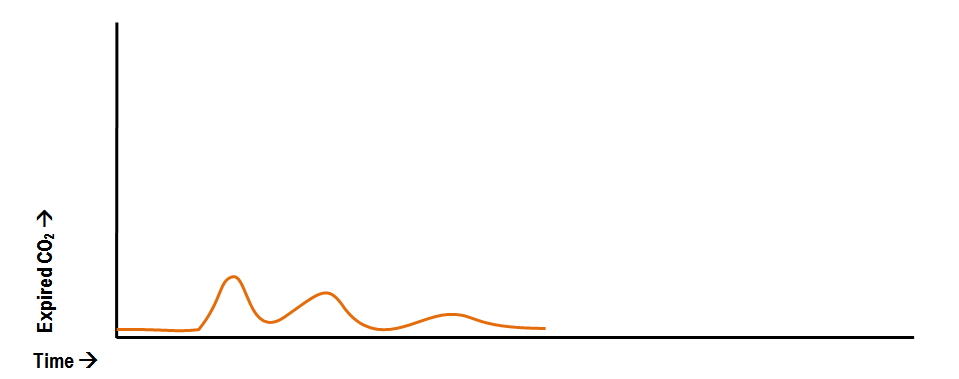
Abnormal Capnography Waveforms And Their Interpretation Deranged Physiology